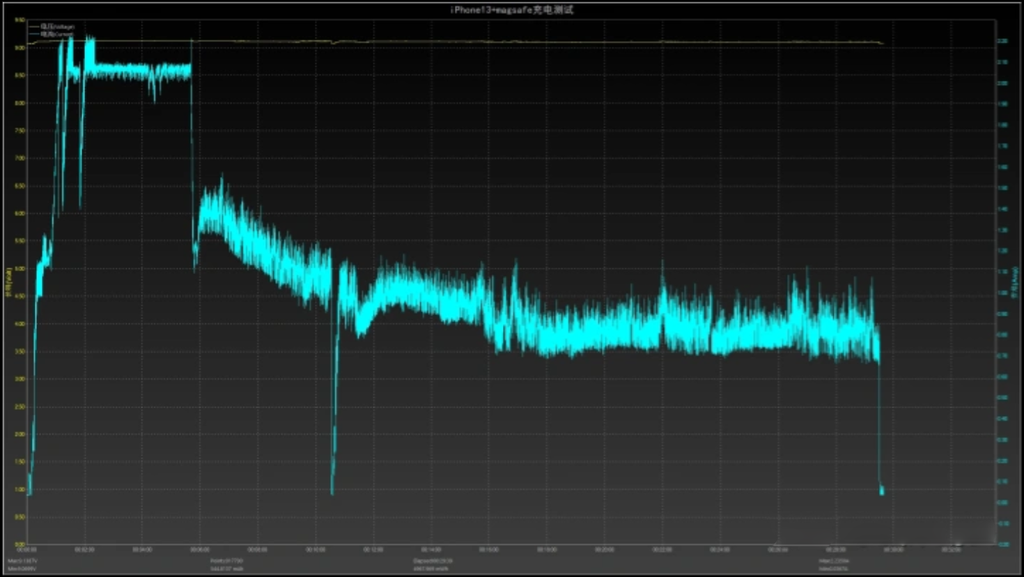
Wireless power banks have revolutionized the way we charge our devices on the go, offering convenience and freedom from tangled cables. However, heat is rapidly generated during wireless charging, causing the output power to drop instantaneously, causing the claimed 15W output power to drop to 4-5W within 5 minutes.
Why Do Wireless Power Banks Generate Heat?
Wireless power banks operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction, allowing them to transfer energy to your device without physical connections. During this process, energy can be lost as heat due to various factors, including:
- Resistance: As electricity flows through the coils and internal components of the power bank, some resistance occurs, leading to heat production.
- Efficiency: Wireless charging isn't 100% efficient, and a portion of the energy is converted into heat instead of being delivered to the device.
- Fast Charging: Many power banks support fast charging, which can generate more heat during the energy transfer process.
- Continuous Use: Users often charge their devices for extended periods, leading to the accumulation of heat inside the power bank.
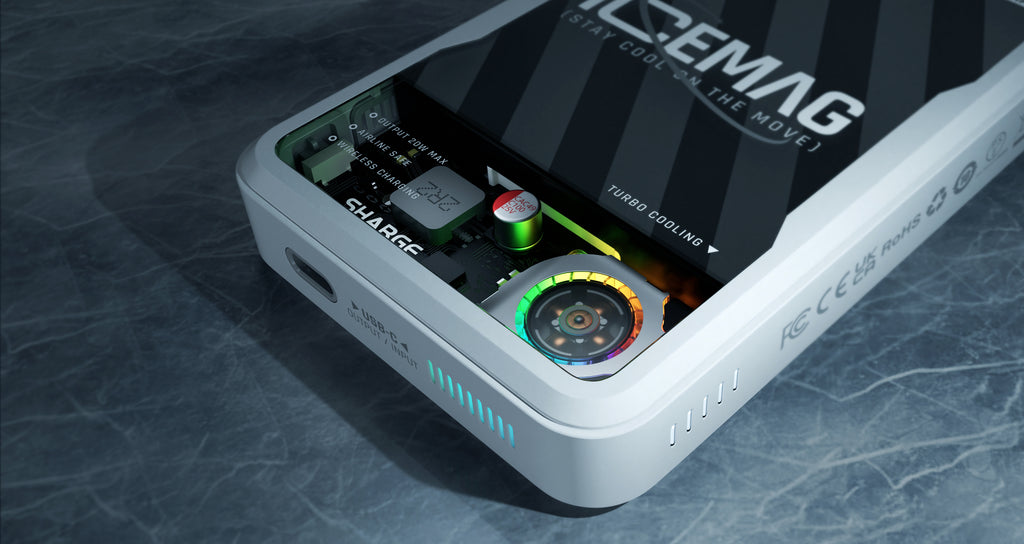
Wireless power banks, like any electronic device that generates or transfers energy, can generate heat during operation, At the same time, the wireless power bank works according to the principle of electromagnetic induction to realize energy transmission, so the heat generation is much greater than that of traditional charging methods; High temperatures can lead to increased internal resistance, reducing the power bank's efficiency and power output. Most manufacturers will choose to actively reduce output power to reduce heat generation when the temperature reaches a certain value, but this has to sacrifice charging speed. Therefore, active cooling is necessary, just like the cooling fans built into smartphones, to ensure that the device operates properly.
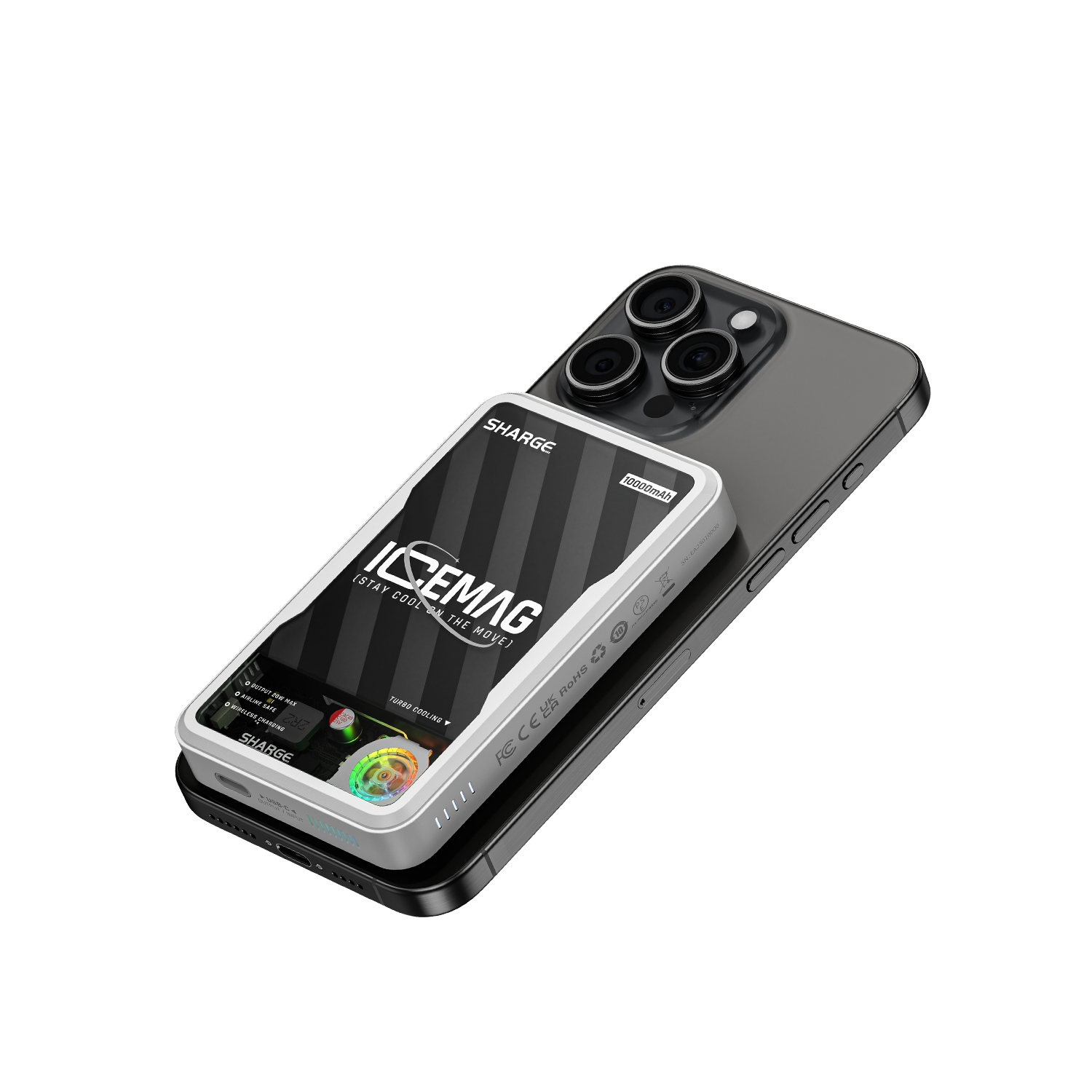
To tackle this issue and ensure optimal performance, the SHARGE ICEMAG wireless power bank integrates an active cooling function with a built-in 8,000 RPM fan. The fan will automatically start when the device starts wireless charging, which can effectively reduce the output power reduction and loss caused by overheating of the device.
The Need for Active Heat Dissipation:
Active heat dissipation in wireless power banks is crucial for several reasons:
- Efficiency: Cooling systems, such as fans, help dissipate heat, improving the overall efficiency of wireless charging. This ensures that more of the energy is transferred to your device, reducing wasted energy.
- Safety: Excessive heat can pose a safety risk. Active cooling prevents overheating, reducing the risk of internal component damage or even fires in extreme cases.
- Battery Health: High temperatures can degrade the internal lithium-ion or lithium-polymer batteries in power banks. Active cooling methods help maintain a safe operating temperature, extending the lifespan of the power bank.
- User Comfort: A hot power bank can be uncomfortable to hold. Active cooling keeps the device at a comfortable temperature.
Wireless power banks have become indispensable in our daily lives, offering a convenient way to keep our devices charged while on the move. However, the generation of heat during wireless charging necessitates active cooling to ensure efficiency, safety, and longevity. The SHARGE ICEMAG Power Bank, equipped with an 8,000 RPM fan, is a prime example of innovative active cooling technology that enhances your charging experience. Stay cool and charged with SHARGE ICEMAG – the future of wireless power banks.








1 comment
Yaagul
Will it work on iPhone15ProMax
Because I just order one ☝️
Leave a comment
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.